Coastal Pioneer Relocation
In early 2021, the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Ocean Observatories Initiative Facilities Board (OOIFB) initiated a process to decide if, and if so where, the Pioneer Array might be relocated to answer pressing science questions and gather data from a new important region. To facilitate community input, NSF and OOIFB held a two-phase Innovations Lab series between January and June of 2021, to determine where the Array might be located and how it might be configured.
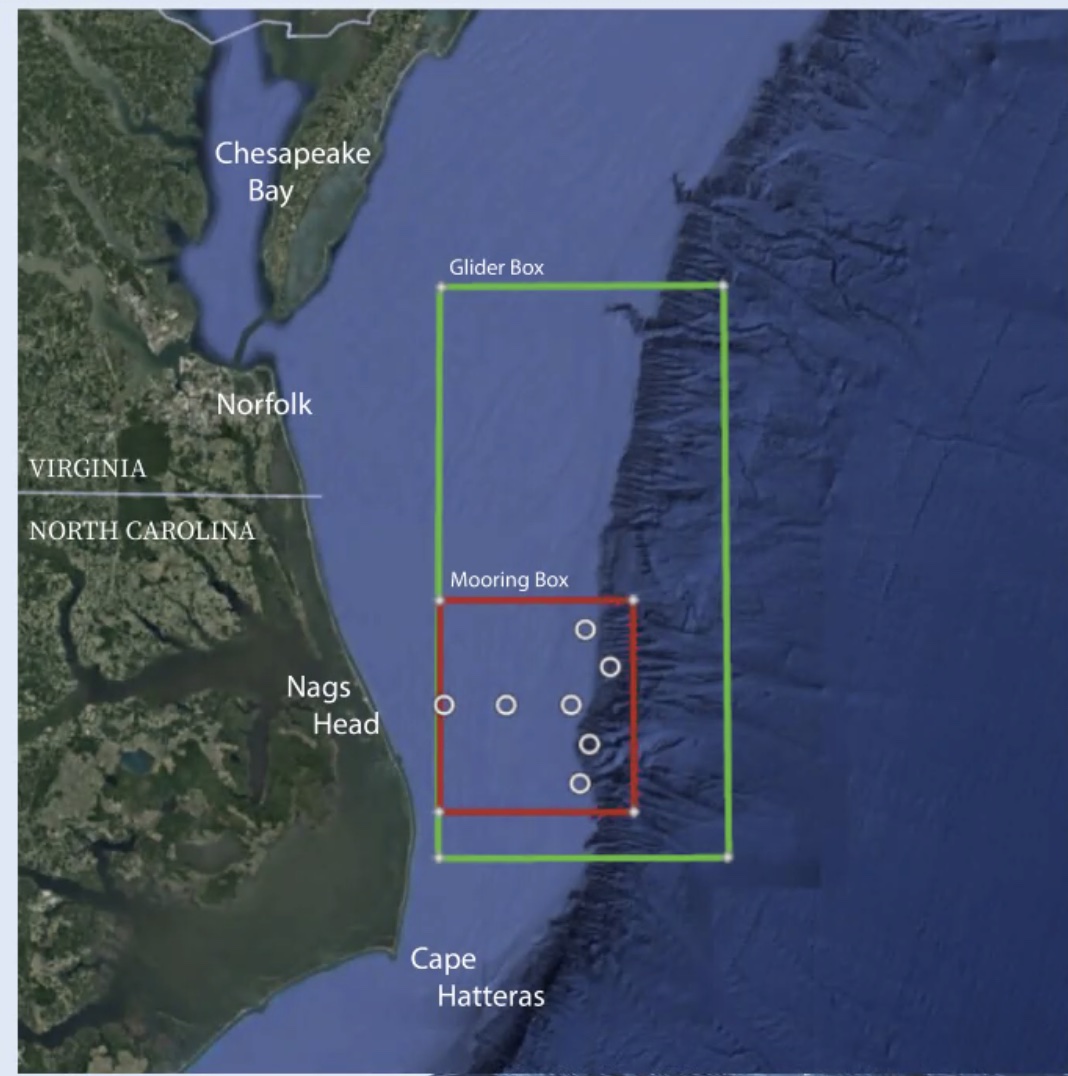
After consideration of input from the first Innovations Lab, held in April 2021, NSF proposed that the Southern Mid-Atlantic Bight between Cape Hatteras and Norfolk Canyon as the next location for the Pioneer Array (see Figure 1). The second Innovations Lab was held in June 2021 to help flesh out science questions, array configurations, and potential partnerships to help inform the planning for a successful relocation. The Mid-Atlantic Bight offers opportunities to collect data on a wide variety of cross-disciplinary science topics including the dynamics of cross-shelf exchange and Gulf Stream influences, processes driving biogeochemical cycling and transport, the ecosystem response to cycling and transport, and the impact of extreme events such as hurricanes and fresh-water outflows. The location also offers opportunities to improve our understanding of hurricane development, tracking, and prediction, and to form partnerships with the nascent offshore wind industry.
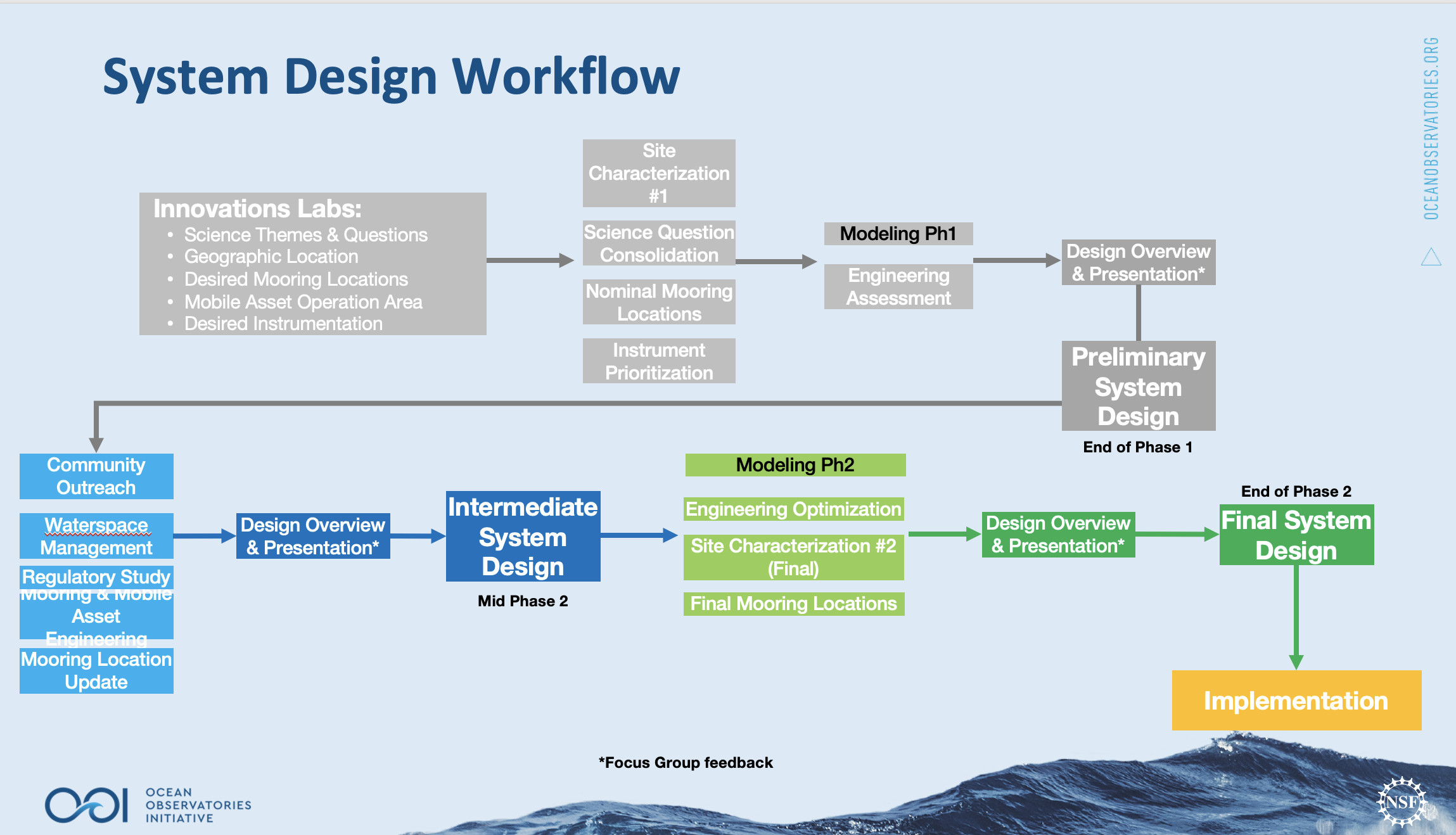
Since June 2021, members of the Coastal and Global Scale Nodes (CGSN) team at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) have been actively working on planning the relocation. The team launched a three-part process to plan for the array deployment at the proposed new location in 2024 as shown in Figure 2. Phase 1 was the planning phase (July 2021-April 2022), during which the team consolidated community input from the Innovations Labs and conducted site characterization and initial engineering assessments for the new site. The team also evaluated environmental regulatory requirements for the proposed new site in advance of submitting environmental compliance documents and permit applications.
Phase 2, the engineering phase, ran from May 2022-December 2022. During this phase, the team completed engineering and design modifications for the moorings, developed instrumentation requirements, and finalized mobile asset plans. They also refined the site characterization and developed a procurement and build schedule. The operation of the New England Shelf Pioneer Array ended in November 2022 to provide time and funding for the redeployment effort.
The implementation stage, Phase 3, began in January 2023 and would end when the array is installed in its proposed new location, scheduled for April 2024. A great deal would be accomplished during this phase, including the successful initiation and conclusion of all environmental compliance (see more details below) and regulatory processes, procurement of materials and instruments, building and field testing of moorings, and ultimately preparation for, and execution of, a cruise to put the moorings in place in the new location.
Environmental Compliance
As described above, NSF proposes to relocate the OOI Pioneer Array to the Southern Mid-Atlantic Bight (MAB) in 2024 (Proposed Action). The Proposed Action would be funded by NSF and implemented through an existing Cooperative Agreement with Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI).
NSF’s proposal to relocate the Pioneer Array to the Southern MAB is currently undergoing environmental review. As part of that process, NSF will comply with various environmental laws and regulatory processes, including but not limited to, the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA), the Coastal Zone Management Act (CZMA), and the Endangered Species Act (ESA).
NSF is currently preparing NEPA documentation for the Proposed Action, which will tier to existing OOI NEPA documentation. When issued, the NEPA documentation for the Pioneer Array relocation to the Southern MAB will be available on the NSF website and the public will be invited to comment on the Proposed Action. NSF will take into consideration all comments received during the open comment period and through other regulatory processes; comments received will be addressed in final NEPA documentation prepared for the action.
Stories recounting the planning process and community input for the Pioneer Array Relocation are available here.
Sites
This array includes following research sites and platforms.