RCA Broadband Provides First Report of Tremor-Like Signals Offshore Cascadia
The recent publication “Possible Shallow Tectonic Tremor Signals Near the Deformation Front in Central Cascadia” (Krauss et al., 2025) presents the first report of tectonic tremor-like signals offshore Cascadia. As described by the authors, deep slow-slip events in Cascadia—lasting from hours to weeks—have been documented by land-based stations for decades. These events can accommodate a significant portion of overall plate motion and may serve as precursors to megathrust earthquakes. Over the past two decades, significant tectonic tremor activity (1–10 Hz) has been observed as a feature of slow slip every 10.5–15.5 months beneath Vancouver Island to northern Oregon (Bombardier et al. 2024), with annual slip events equivalent to a magnitude ~6.5 earthquake. These typically occur well inland, at depths of approximately 30–40 km. Contrastingly, it is unknown whether slow-slip events and accompanying tectonic tremor occur at shallow subduction depths in the offshore region.
Krauss et al. (2025) analyzed data collected 2015-2024 from buried ocean-bottom seismometers (OBS) at two sites: Slope Base (2,920 m depth), located 5 km seaward of the deformation front, and Southern Hydrate Ridge (790 m depth), approximately 20 km landward. The analysis incorporated in-situ bottom current data. After applying short- and long-term averaging techniques, the study identified 85,000 signals at Slope Base and 30,055 at Southern Hydrate Ridge, encompassing T-phase events, ship noise, and tectonic tremor-like signals. Notably, tectonic tremor-like signals were observed exclusively at Slope Base.
These signals cannot be attributed to ship traffic or environmental noise. Instead, they are hypothesized to originate from slow slip on one of many nearby tectonic structures: the décollement fault, faults near the subduction zone front and outermost accretionary wedge, faults on the incoming Juan de Fuca Plate, or nearby strike-slip structures such as the Alvin Canyon Fault. However, without additional observations of these signals on multiple stations, it is unclear whether they are tectonic or represent another signal altogether.
Future deployments, such as those planned through the Cascadia Offshore Subduction Zone Observatory (COSZO) will improve our ability to pinpoint the sources of these offshore tremors. The full dataset and results are available on GitHub (https://github.com/zoekrauss/obs_tremor) and archived on Zenodo (https://zenodo.org/records/14532861).
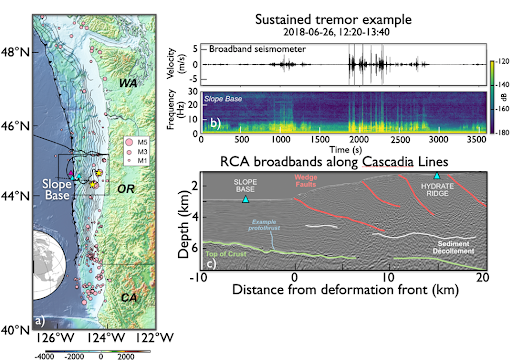
Figure 1. a) Location of the Regional Cabled Array cabled broadband seismometers (OBS’s -cyan triangles) offshore Newport Oregon and an autonomous instrument (purple triangle), earthquakes (pink circles) and along and just offshore the Cascadia Margin. b) sustained tremor-like signals from the broadband at Slope Base. c) Subsurface structure across strike of the margin showing location of Slope Base and Southern Hydrate Ridge OBS’s, accretionary margin faults and demarcation of a boundary interpreted to be a protothrust between the sedimentary column and the incoming Juan de Fuca Plate crust.
___________________
References:
Krauss, Z., Wilcock, W.D.S., and Creager, K.C. (2025) Possible shallow tectonic tremor signals near the deformation front in Central Caldera. Seismica, https://seismica.library.mcgill.ca/article/view/1540.
Bombardier, M., Cassidy, J.F., Dosso, S.E., and K. Honn (2024) Spatial distribution of tremor episodes from long-term monitoring in the northern Cascadia Subduction Zone. Journal of Geophysical Research, https://doi.org/10.1029/2024JB029159.
